Has video resolution always mattered? Or is it a phenomenon gaining importance after technological advancements?
Video resolution did not matter until technology upgraded with multiple grades of video quality. In the beginning of the 1900s, people perceived the quality of video to be good and they were amazed, even though it was poor in comparison to today’s standards. Over the years, this scenario has been completely changed.
In the current day, there are about 10 grades of resolutions from commercial to industrial use. The availability of options in video quality, downplayed lower grade qualities and demanded high quality. This shift is evident in the debate between HD vs SD TV, where standard definition has gradually faded in favor of superior clarity and detail. While technological advancements were vertical, multi-option qualities were horizontal innovation.
In this blog, we’ll explore the primary video qualities and their related concepts. Understanding this will help you render your VOD/OTT platform for better SEO ranking and eventually more website traffic.
Video resolution has undergone 7 major generations since 1888 from mechanical TV with 30 lines to 8K UHD with 33 million pixels.
Key takeaways from HD video vs SD video resolutions
- The progress of video resolution has been significant. With 7 major generations, a broad range of resolutions offer suitability to different users from SD to 16K immersive experience.
- When comparing HD vs SD TV, the difference lies in clarity and detail. Higher resolutions like HD, UHD, 4K, 8K are preferred in modern devices like Smart TVs and smartphones to provide a clearer and more detailed viewing experience.
- Resolutions are progressive, as they increase, more bandwidth and storage are required. This contrast between high and low resolutions highlights the need for the speed of the internet.
- AI-powered videos are transforming the way content is consumed. Features like immersive AR/VR experiences, shoppable videos, and personalized recommendations are becoming common to enhance user engagement.
- The future of the video industry will feature 8K and 12K content. This will provide more immersive, efficient, and interactive content creation and consumption.
What is SD?

SD (Standard Definition) refers to a resolution lower than HD (High Definition). SD resolution translates to 480p i.e., 854×480 pixels.
Key Characteristics of Standard Definition:
- Low pixel density
- Lower video quality compared to modern standards
- Displayed in 4:3 aspect ratio
- Often associated with older TV broadcasts, DVDs, and video tapes
Around 5-10% of video streaming content is still viewed in SD, mainly due to bandwidth limitations and mobile data savings.
What is HD?

High Definition (HD) refers to a resolution that provides a higher level of detail and clarity compared to Standard Definition (SD). HD translates to 720p i.e.,1280×720 pixels.
Key Characteristics of High Definition:
- Higher pixel density
- Improved video quality
- Displayed in widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9
- Support for higher frame rates
Over 80% of global internet users watch videos in 1080p or higher
How Many Grades of Video Quality Exist in 2025?
Low-Quality Resolutions
- 144p (240×144): Very pixelated, used for low-bandwidth streaming.
- 240p (426×240): Low-resolution, poor clarity, used in older mobile videos.
- 360p (640×360): Basic SD quality, used on low-quality streaming settings.
Standard Definition (SD) Resolutions
- 480p (854×480): DVD quality, decent for small screens.
High Definition (HD) Resolutions
- 720p (1280×720) – HD: Basic high-definition, used in older HDTVs.
- 1080p (1920×1080) – Full HD (FHD): Used in Blu-ray discs, online streaming, and HDTV broadcasts.
Ultra High Definition (UHD) Resolutions
- 1440p (2560×1440) – Quad HD (QHD or 2K): Used in gaming monitors and high-end smartphones for enhanced visuals.
- 2160p (3840×2160) – 4K UHD: Standard for premium TVs, cinematic productions, and high-end streaming services.
Cutting-Edge Resolutions
- 4320p (7680×4320) – 8K UHD: Ultra high-end, used in premium filmmaking and experimental broadcasts.
- 12K & 16K: Used for specialized cinematic production and future-proofing.
Based on your type of content and the target audience, you can choose to stream your content in any resolution grade with Webnexs’ white-label solution. Start with a demo from our team.
HD vs. SD TV: Key differences
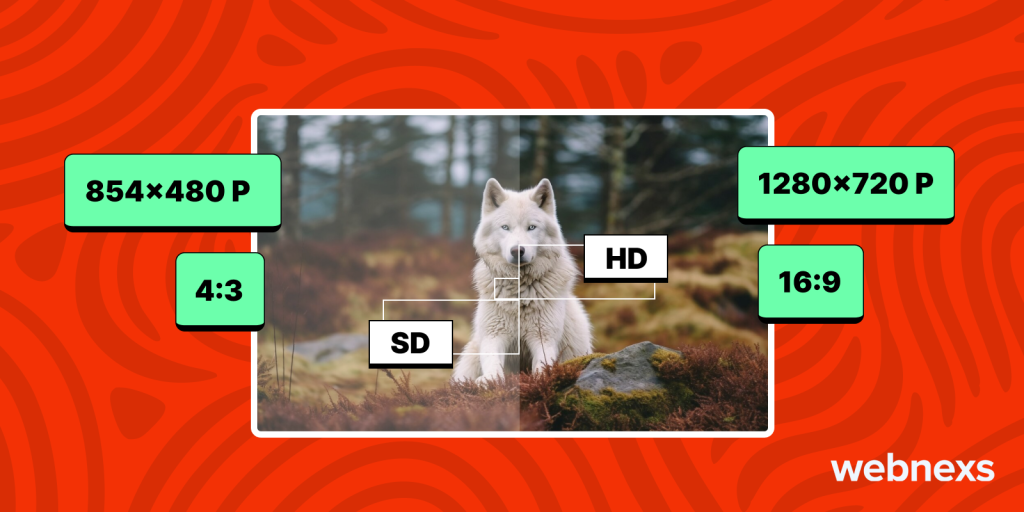
1. Resolution
HD: 1280×720
SD: 854×480
HD vs SD TV differs significantly in terms of pixel count, which directly impacts video clarity.
2. Image Quality
HD: Sharper, clearer images with more details and less pixelation.
SD: Lower sharpness, visible pixelation, and less clarity.
In HD video vs SD video comparison, HD delivers better visual fidelity for a quality viewing experience.
3. Aspect Ratio
HD: 16:9
SD: 4:3
The HD vs SD TV difference is most noticeable when older content is played on modern widescreen displays.
4. Bandwidth & File Size
HD: Larger file sizes and requires more bandwidth for streaming.
SD: Smaller file sizes, less bandwidth consumption.
For users with limited internet speed, opting for HD video vs SD video becomes a matter of balancing quality with accessibility.
5. Streaming & Compatibility
HD: Requires higher-speed internet for smooth playback.
SD: Works on lower bandwidth connections and older devices.
Many streaming services allow users to toggle between HD vs SD TV settings, depending on their connection speed.
6. Storage Requirements
HD: Takes up more storage space on devices.
SD: Consumes less storage.
Content creators must consider storage limitations when choosing between HD video vs SD video formats.
7. Use Cases
HD: Preferred for streaming, gaming, movies, and professional content.
SD: Used for legacy broadcasts, older DVDs, and low-bandwidth streaming.
When deciding between HD video vs SD video, content creators must weigh the target platform and audience’s internet capabilities.
Aspect Ratio: HD video vs SD video
HD Video Aspect Ratio
- Common Aspect Ratio: 16:9
- Resolution Examples:
- 1280×720 (720p HD)
- 1920×1080 (1080p Full HD)
- 3840×2160 (4K UHD)
- Characteristics:
- It has a widescreen format, making it suitable for modern TVs, computers, and streaming platforms.
- Offers better clarity, sharpness, and color accuracy.
- Ideal for cinematic experiences and digital content.
The HD vs SD TV aspect ratio difference is crucial for content compatibility across multiple devices.
SD Video Aspect Ratio
- Common Aspect Ratio: 4:3
- Resolution Examples:
- 640×480 (480p SD)
- 720×576 (PAL SD)
- 720×480 (NTSC SD)
- Characteristics:
- More square-like format, used in older televisions and early digital media.
- Lower resolution and quality compared to HD.
- Less suitable for modern screens, as black bars (pillarboxing) may appear on widescreen displays.
When analyzing HD video vs SD video, it’s clear that HD’s widescreen format aligns better with modern display technology.
Frame Rate Differences: HD vs. SD TV
1. Storage Requirements
SD: Requires 3-4 times lower storage space
HD: Requires much more storage.
This makes HD video vs SD video a critical consideration for users with limited storage capacity.
2. Bandwidth Usage
SD: Uses about 1-2 Mbps per stream.
HD:
- 720p: Requires 3-5 Mbps.
- 1080p: Needs 5-8 Mbps.
- 4K UHD (if applicable): Requires 15-25 Mbps.
HD vs. SD TV both impact data usage, making SD a practical choice for low-bandwidth users.
3. Cost Considerations
SD: Lower storage and bandwidth costs, making it ideal for budget-conscious streaming services.
HD: Higher costs due to increased data transfer and storage needs.
For businesses and consumers, choosing between HD video vs SD video is a financial decision, balancing quality and cost-efficiency.
4. User Experience & Compatibility
SD: Suitable for mobile devices, slower internet speeds, and regions with bandwidth restrictions.
HD: Preferred for large screens and premium user experiences but requires better network conditions.
When deciding on HD vs SD TV, users must consider device compatibility and network speed to ensure smooth playback.
5. Content Type Considerations
SD: Suitable for news, educational content, or low-motion videos.
HD: Suitable for high-motion content such as movies, sports, and gaming.
Choosing between HD video and SD video depends on the type of content. Fast-paced visuals demand HD, while static content can perform well in SD.
Device Compatibility
- Supported Devices
HD video vs SD video: HD video is supported on smartphones, modern TVs, tablets, laptops, gaming consoles, and streaming devices, while SD video works on older TVs, basic feature phones, older DVD players, and legacy devices.
- Internet Connection Requirement
HD video vs SD video:HD video requires higher bandwidth, whereas SD video works with lower bandwidth.
3. Mobile Device Compatibility
HD video vs SD video: HD video is optimized for modern smartphones and tablets with HD screens, while SD video works on budget smartphones and older mobile devices.
4. Smart TV & Streaming Support
HD video vs SD video: HD video is required for most OTT platforms and modern streaming services, but SD video is often an option for users with slower internet, though it is less prioritized.
5. Gaming Consoles
HD video vs SD video: HD video supports PS5, Xbox Series X, and newer gaming setups, whereas SD video is compatible with older gaming consoles and basic streaming modes.
Display Support
- Screen Adaptability
HD video vs SD video: HD video performs well on large screens without pixelation, whereas SD video loses clarity on large screens and is best suited for small displays. - Aspect Ratio
HD video vs SD video: HD video typically uses a 16:9 widescreen format, while SD video can be either 4:3 or 16:9, depending on the content source. - Color & Detail
HD video vs SD video: HD video offers sharper details, better contrast, and more vibrant colors, whereas SD video has less color accuracy, lower detail, and visible compression artifacts. - Playback Performance
HD video vs SD video: HD video requires powerful processors for smooth playback, while SD video can run smoothly on older hardware.
Streaming and Broadcasting:HD video vs SD video
1. Resolution Differences
- HD: 720p (1280×720 pixels) and 1080p (1920×1080 pixels).
- SD: 480p (720×480 pixels) or lower.
2. Video Quality and Clarity
- HD: Provides sharper, clearer images and better color depth.
- SD: Video may appear pixelated or blurry on larger screens.
3. Bandwidth and Streaming Requirements
- HD: Requires 3-6 Mbps for 720p, 5-10 Mbps for 1080p.
- SD: Requires (1-2 Mbps) for 480p
4. Storage and Processing Power
- HD: Files are larger and demand more storage and powerful hardware.
- SD: Files are smaller, making them easier to store and stream with less processing power.
5. Device Compatibility
- HD: For modern TVs, smartphones, and streaming platforms.
- SD: Works on older devices with lower resolution displays.
6. Cost and Monetization Impact
- HD: Requires more resources, leading to higher costs for storage and delivery.
- SD: It comes with the basic plan which costs much less than the others.
Bitrate: HD video vs SD video
| Resolution | Bitrate (Standard Streaming) | Bitrate (High-Quality Streaming) |
| 144p | 80-100 Kbps | 150-200 Kbps |
| 240p | 300-500 Kbps | 500-700 Kbps |
| 360p | 600-1,000 Kbps | 1-1.5 Mbps |
| 480p (SD) | 1-2 Mbps | 2.5 Mbps |
| 720p (HD) | 3-6 Mbps | 5-7 Mbps |
| 1080p (Full HD) | 5-10 Mbps | 8-12 Mbps |
| 1440p (2K) | 12-15 Mbps | 16-20 Mbps |
| 2160p (4K UHD) | 15-25 Mbps | 25-35 Mbps |
| 4320p (8K UHD) | 50-80 Mbps | 80-100 Mbps |
| 12K & 16K | 100-200 Mbps | 200+ Mbps |
Cost Differences: HD vs. SD TV
1. Hardware Costs
- TV Set
- SD TV: Cheaper
- HD TV: More expensive
- Streaming Devices
- SD TV: Basic models
- HD TV: Higher-end models
- Cable/Satellite Box
- SD TV: Basic SD boxes are cheaper
- HD TV: HD-enabled boxes cost more due to better hardware
2. Subscription Costs (Cable & Streaming Services)
- Cable TV Packages
- SD TV: Lower cost
- HD TV: Higher cost
- Streaming Services
- SD TV: Basic plans are cheaper
- HD TV: HD/4K plans cost more
- Pay-Per-View (PPV) & Rentals
- SD TV: Lower-cost SD rentals
- HD TV: HD movies and events cost more
3. Data Consumption & Internet Costs
- SD (480p): ~0.7 GB/hour – Lower data usage, cheaper internet plans work fine
- HD (720p/1080p): ~1.5-3 GB/hour – Requires higher bandwidth, may need a more expensive internet plan
- 4K UHD: ~7-16 GB/hour – Very high data consumption, costly internet plans required
4. Storage & Distribution Costs
- HD: Files are larger, increasing hosting and content delivery costs for broadcasters and OTT platforms.
- SD: Files are smaller, requiring less cloud storage, server space, and bandwidth.
Video Upscaling: Turning SD Content Into HD
How Video Upscaling Works
Upscaling increases a video’s resolution by interpolating missing pixels. Advanced algorithms analyze the original pixel structure and predict new ones to enhance the resolution without distorting the image. AI and machine learning improve the quality, making the video sharper and more defined.
Upscaling Technologies
- Hardware Upscaling:
Built-in upscaling engines in devices enhance SD or 720p content to 1080p or 4K.
- Software Upscaling:
Editing software uses algorithms to upscale the resolution and reduce artifacts.
Pros:
- Improved viewing experience on HD or 4K screens.
- Older content is compatible with modern devices.
- Cost-effective for viewing content in higher resolutions.
Cons:
- Limited improvement, as it can’t add new details.
- Artifacts like blurriness or pixelation may appear, especially with lower-quality upscaling.
The difference between hd video vs sd video is crucial for content creators, as choosing the right aspect ratio and resolution impacts the viewing experience. While hd vs sd tv remains a deciding factor for many users, modern devices favor higher resolutions.
Future of Video

1. Higher Resolutions & Immersive Experiences
- Streaming in 8K and 12K will become mainstream as display technology improves, offering a significant upgrade over current HD vs SD TV capabilities.
- Colour accuracy and contrast can be enhanced with HLG, Dolby Vision, and other technologies, advancing the quality of HD video vs SD video.
- Immersive video experiences can also be created with Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), pushing the boundaries of video quality beyond what HD video vs SD video currently offers
2. AI & Machine Learning in Video Production
- Professional-level production can be executed faster, making it more accessible with automated editing tools.
- AI-powered video creation will change how content is created, distributed, and consumed in marketing, entertainment, and personalized content.
- User-engagement can be enhanced in streaming platforms with AI-driven personalization.
3. Streaming Evolution: 5G & Edge Computing
- Faster mobile networks will enable ultra-HD live streaming with minimal buffering.
- Decentralized processing will reduce latency, improving video delivery quality.
- More studios and broadcasters will shift to cloud-based video workflows.
4. Interactive & Shoppable Videos
- Video-integrated e-commerce platforms will enable users to shop directly from videos, with HD video vs SD video offering different viewing experiences for consumers.
- Engagement-fostering activities include quizzes, clickable links, and real-time audience participation.
- Interactive storytelling will become more common.
5. Decentralized & Blockchain-Powered Video
- Decentralized platforms using blockchain to prevent censorship and improve creator earnings will support various video formats, with HD video vs SD video providing distinct quality levels for different user needs.
- Content creators may sell exclusive video NFTs for ownership rights.
6. Sustainable & Efficient Video Processing
- New formats like AV1 and VVC will reduce file sizes while maintaining quality.
- Streaming services will adopt greener infrastructure to cut carbon emissions.
Statistics on Video quality and adoption:
- Less than 10% of households globally still use SD-only TVs.
- Over 85% of households have HD or higher-resolution TVs.
- 50% of households in the U.S. & Europe have a 4K TV.
- Global 4K penetration is expected to reach 75% by 2030.
- 8K TV adoption is still below 5% globally, mainly due to limited content availability.
Wrapping up
From the early days of mechanical TV to the rise of 4K and 8K UHD, the demand for higher resolution has grown alongside better viewing experiences and higher expectations for quality. While video content has been consistent for a century, the dynamic nature of technology has led to continuous advancements that resulted in several generations of resolutions for improved clarity of video.
This means that there is opportunity for all pricing ranges to offer quality for every type of audience. With the future bringing more advanced resolutions, interactive content, and AI-driven improvements, the video industry is changing to offer users more engaging, customized, and high-quality experiences. HD video vs SD video comparison sheds light on the significance of the quality of the viewing experience and the demand for that quality experience.
There is a market for all types of content quality. Launching your platform is the first step towards grabbing a monetizable market. Explore Webnexs’ white-label solution for a quick time-to-market. A free demo with our team will help you uncover the advantages of our solution.


