Hey, idea seekers!
62% of ecommerce businesses have adopted microservices architecture
According to IMARC Group, the global microservices architecture market is projected to grow from USD 4.2 billion in 2024 to USD 13.1 billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.7% during 2025-2033.
Have you heard about Ecommerce Microservices Architecture?
In this blog, we’ll explain what it is with examples to make it easy to understand. It’s a great resource for retail business owners and ecommerce merchants who want to improve their online stores.
You’ll learn how this approach can help your business run more smoothly, grow easily, and stay competitive. While each microservice typically manages its own database, we’ll also touch on the specific circumstances where multiple microservices might share a single database.
Whether you’re just starting or already managing an ecommerce platform, this guide will give you practical insights to build a stronger, more efficient system for your business.
Key Takeaways On Ecommerce Microservices Architecture
- Ecommerce Microservices Architecture makes it easier for businesses to stay flexible and quickly respond to market changes, all without disrupting daily operations.
- By dividing the system into separate services, it ensures that if one service fails, it won’t take down the entire system, boosting stability.
- Ecommerce Microservices Architecture makes it easy for businesses to adjust their services based on customer demand, which boosts performance and helps prevent system overloads.
- Modular design of ecommerce microservices architecture allows businesses to easily manage services, enabling quick updates or changes without disrupting the entire system and speeding up feature launches.
- This architecture encourages companies to innovate, as it gives them the flexibility to try out new technologies and stay competitive in a fast-moving market.
Scale Seamlessly with Ecommerce Microservice Architecture!
What is Ecommerce Microservices Architecture?
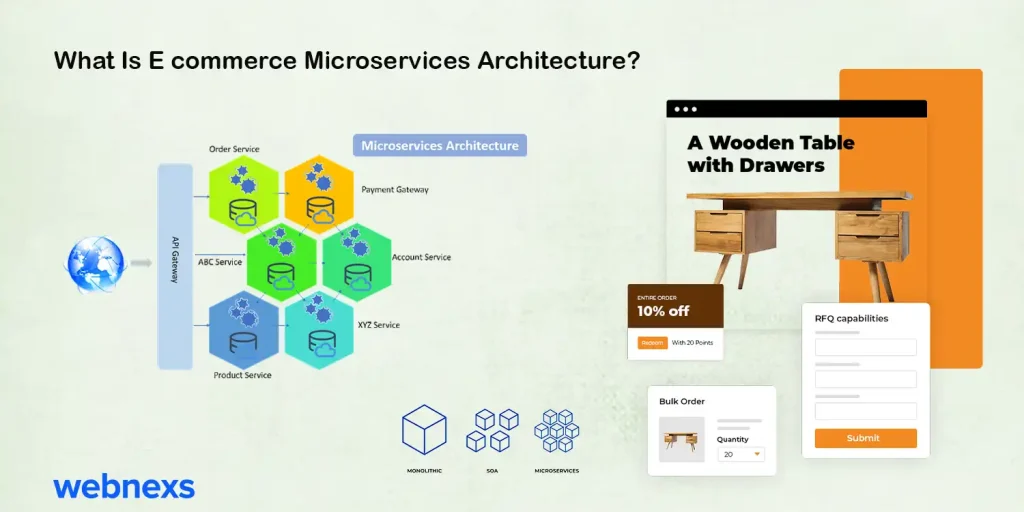
Ecommerce microservices architecture is a way of building ecommerce software where each part of the system operates separately. Unlike traditional monolithic systems, where key features like shopping carts, product listings, and payment processing are all connected to the same system, microservices allow each feature to run independently.
In a monolithic system, updating or changing something in the backend can affect the user interface, cause website downtime, and slow down development. These systems also limit customization and make it harder to adapt to new trends or technologies quickly, especially as marketplace trends continue to evolve and demand faster, more flexible solutions.
With microservices, developers can add new features to the backend without affecting the rest of the system. This allows for easier customization and scaling of the platform.. Services can be added as needed, making the system more adaptable and “future-proof.”
The global microservices architecture market is projected to reach $21.67 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 18.6% from 2021 to 2030. By 2026, it is estimated that 90% of new applications will be developed using microservices architectures to improve scalability and agility.
Read More: What Is Headless Commerce Architecture, And Why Is It The Future?
5 Key Advantages for E commerce Microservice Architecture

1. Reduced Software Complexity
A single microservice contains limited functionality. It makes maintenance and updating much more manageable. You only need to worry about messages from other microservices to which you have a sign (inputs) and your API management, which can be called (outputs).
72% of organizations reported that microservices architecture simplified their software maintenance and made it easier to scale individual components.
2. Specialization
Microservices enable you to select the best tool for the job. Each microservice can have its language, framework, or ancillary services preferred by the team. Java, for example, could be used by developers for services requiring extensive background calculation. Others may rely on more lightweight technologies such as PHP or Ruby.
60% of eCommerce companies experienced improved developer productivity because of the ability to use specialized tools tailored for individual microservices.
3. Faster Time To Market
Creating a microservice necessitates a multidisciplinary development team that works independently on their project. It reduces team synchronization efforts and allows for significantly quicker deployment.
For example, the product and service team can work independently, making adjustments and automating deployments as needed – regardless of what the payment team is currently working on.
50-60% time-to-market is reduced on average using microservices according to a report by McKinsey
4. Increased Stability
A business application comprised of a collection of microservices has no single point of failure. If one service stops responding, the application does not automatically fail.
You can, for example, continue watching movies on Netflix even if the search is unavailable. Maintenance, failure, and security will not have the same impact on users as they would with a monolithic architecture.
99.9% uptime rate and high customer satisfaction despite scaling to millions of users were achieved by Netflix.
5. Highly Scalable
Microservices for ecommerce are small and identified. It makes it easier to scale them vertically and improve business application performance. It can deploy business-critical services across multiple servers for increased availability and performance.
70% of companies leveraging microservices see a 50% improvement in scalability and performance.
Benefits Of Using Ecommerce Microservices Architecture

As customer demands evolve, and mobile web usage increases, businesses must have a robust operational and technological framework that supports both resilience and speed. Speed has become a crucial factor in staying competitive.
Traditional monolithic ecommerce applications, used by many large retailers, are hindering innovation. In contrast, ecommerce microservice architecture allows businesses to adapt and scale their online stores quickly.
This flexibility enables companies to test new tools and features without impacting the entire system.
Here are some of the key benefits of ecommerce microservices:
1. Consistency
Since microservices operate independently, they can be troubleshooted without impacting the rest of the system. This enhances stability as any issue within a single service won’t affect the entire modern ecommerce architecture.
Each microservice can be built, tested, and deployed separately, ensuring that the rest of the platform remains unaffected.
2. Faster Time to Market
Businesses can easily test new tools and technologies using decentralized microservices. Developers aren’t restricted to a specific system or programming language, making it faster to add modern ecommerce website features and stay ahead of customer expectations.
This method enables quick testing and implementation of new functionalities without requiring a complete system overhaul.
3. Scalability
The modular design of microservices for ecommerce makes scaling simpler and more efficient. Businesses can roll out new features and components flexibly, leading to a faster time to market for innovative ideas that differentiate them from competitors.
Microservices architecture for ecommerce allows for specific areas of the platform to scale independently based on demand.
4. Reduced Maintenance
Adding new features becomes simpler, and the chances of system-wide downtime are greatly reduced. If one part of the system faces an issue, the rest can keep running smoothly, ensuring better reliability. Maintenance tasks can also be done without interrupting the entire platform, minimizing operational risks.
5. Simplified Codebase
In contrast to monolithic systems, where any significant update requires reworking the entire software, commerce microservices architecture allows for isolated updates.
This reduces the complexity of the codebase and ensures smoother maintenance, enabling businesses to keep their systems running smoothly while introducing new features.
Overall, ecommerce microservices architecture provide unparalleled flexibility, allowing businesses to implement the best-suited solutions for their products, services, and operational needs.
14 Key Components of Ecommerce Microservices Architecture
1. User Interface (UI)
It is part of the presentation layer, i.e., the front end where the customers interact with the ecommerce platform. The elements included are product lists, carts, user accounts, billing, order status, refund initiation, and other pages.
Single Page Applications (SPA) or Progressive Web Apps (PWA) are commonly used in modern ecommerce architecture to build this UI layer using a microservices approach. This strategy enhances performance and provides a seamless user experience by reducing page reloads and enabling dynamic content updates.
These interfaces are often developed with client-side frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js. For mobile platforms, native development tools for Android and iOS can also be used to create responsive and user-friendly applications making it easier for customers to access your ecommerce services across devices.
RESTful or GraphQL APIs are then used to connect the front end with backend services, allowing users to browse, shop, and manage their accounts efficiently.
Single Page Applications (SPAs) improve page load speed by up to 67% compared to traditional websites.
2. Microservices
Microservices themselves are services that can be deployed independently to handle specific business functions. In the context of microservice architecture for ecommerce, this approach accelerates development cycles and simplifies scaling or replacing individual services.
Each microservice focuses on a particular aspect of the entire process, such as inventory management, user authentication, or order processing, and operates autonomously. To simplify, here are a few examples:
- Product management
Manages product catalogs, descriptions, prices and images.
- Order processing
Mandates the creation and management of orders from shipping to tracking status.
- Payment gateway
Enables secure transactions and integrations with third-party payment providers.
- Logistics
Manages shipping address, tracking numbers and coordinates with logistics providers.
Companies using microservices report a 50% increase in application scalability.
3. API Gateway
It is a crucial component in ecommerce microservice architecture, serving as a reverse proxy. Client requests require an entry point and APIs are utilized for that and the same is routed to the right microservice.
In simple terms, the gateway enhances the security and performance of the headless ecommerce platform. It handles various tasks, which are listed below.
- Authentication and authorization
It ensures that the users are properly authenticated and authorized to access resources.
- Rate limiting
It prevents abuse by limiting the number of requests that a user can initiate in a particular time frame.
- Load balancing
It is used to distribute the incoming traffic across multiple instances of microservices.
- Response aggregation
It consolidates responses from multiple microservices into a single response for the client.
API gateways can reduce response times by up to 35%, improving customer satisfaction.
4. Database per service
The functional aspect of an commerce microservice architecture works by enabling each service to manage its own database. This allows for each microservice to independently scale leaving others unaffected.
One thing to consider is that the database used for different services within each microservice differs based on requirements.
The two major types are SQL Databases and NoSQL Databases. This enables each microservice to function efficiently as the limitations associated with the monolithic architecture are eliminated completely.
Using decentralized databases can reduce latency by up to 40%, especially during high-traffic events.
5. Service discovery
Microservices play a pivotal role in scaling a microservices ecommerce platform. As the platform grows, service discovery becomes essential to help microservices locate and communicate with one another efficiently.
This is achieved by maintaining an updated list of their specific locations. Tools like Eureka and Consul facilitate these connections by allowing services to interact without relying on fixed addresses, even as new services are added or existing ones are moved.
Service discovery tools like Consul or Eureka reduce microservices communication latency by 30%.
6. Message broker/queue
Asynchronous communication between services is better than the API calls used in monolithic architecture to decouple and improve reliability. Message brokers such as Kafka or RabbitMQ facilitate this function in microservices architecture for ecommerce.
It adds advantages by reducing the potential of encountering bottlenecks and strengthens the resilience of the system. Even if one of the services fails to operate, others can continue without any hindrances.
Asynchronous communication improves system resilience by up to 45%.
7. Authentication and authorization service
Security threats are attacks that can cause sensitive information to be breached. These details include customer information, payment details, and other transaction records. By ensuring that only authorized users gain access, potential threats can be mitigated. OAuth and JWT can be deployed to ensure secure authentication and authorization.
OAuth facilitates secure access delegation, while JWT is commonly used for stateless user authentication across services. If integrated with external identity providers, customer logins and permissions can be managed efficiently.
This system performs complete verification of user identity and permissions before granting access to resources or allowing specific actions, thereby enhancing overall security in microservice architecture for ecommerce.
OAuth and JWT reduce unauthorized access incidents by 60%.
8. Payment gateway integration
The most sensitive component of an ecommerce platform is the payment and transaction system. Integrating the payment gateway microservice with third-party payment providers is crucial to ensure seamless and secure transaction completion.
Only payment gateways that comply with industry standards, such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), should be trusted to handle transactions.
Due to its critical nature, this service in microservices ecommerce is isolated to enhance security and reliability, and its scaling is managed independently from other components to handle peak loads efficiently.
Payment failures are reduced by 25% with isolated payment microservices.
9. Search service
Fast and efficient search functionality is provided by this component in the ecommerce platform. Advanced search capabilities are utilized by modern ecommerce platforms, allowing customers to use the filter option in their browsing experience.
High performance and full-text search results from using search engines like Elasticsearch, which index product data. This is an illustration of its implementation. The platform is enabled to maintain a responsive experience under heavy loads by transferring search operations to a dedicated service.
Advanced search and filtering capabilities increase conversion rates by 21%.
10. Inventory management service
It functions as an escort for managing accurate stock levels and preventing over-selling. Additionally, it tracks product availability in real-time, manages stock levels across multiple warehouses and coordinates restocking procedures.
Furthermore, order and shipping services, when integrated with the inventory service, ensure products are updated on their status. This is also responsible for providing customers with product availability information while browsing the platform.
Platforms with automated restocking improve stock availability by 45%.
11. Shipping and logistics service
This component coordinates with the shipping and delivery process for orders. By calculating shipping costs, selecting the shipping provider, and generating tracking numbers, it provides detailed information during the checkout process.
By integrating with third-party logistics, it provides customers with real-time tracking information. During peak seasons, when there is heavy traffic, it ensures that higher transaction volumes are efficiently handled.
92% of customers expect real-time shipping updates during their purchase journey.
12. Analytics and reporting service
Different microservices in ecommerce are used to fetch data to provide business insights and performance metrics. Customer behaviour, sales, inventory levels and system performance related data are gathered to enable useful analysis.
Real-time dashboards and business intelligence are offered by integrating with the service using tools like Google Analytics or Tableau.
Informed decisions can be made about pricing, marketing strategies, product offerings and overall platform improvements. This is possible by the data-driven approach that helps ecommerce.
Businesses using analytics services see a 37% increase in operational efficiency.
13. Cache layer
As part of the performance-enabling component, a Cache Layer is utilized to store frequently accessed data temporarily to reduce the load on the backend database and improve response times.
Especially during high traffic periods like the festive season when the demand is high, the caching mechanism improves the speed and performance of the platform in microservice architecture for ecommerce.
Platforms implementing a caching layer reduce backend load by 60%.
14. CI/CD Pipeline
It is a set of automated processes for integrating and deploying code changes into production. Rapid and safe development, testing, and deployment of microservices can be ensured.
As a result, it enables ecommerce microservices architecture to deploy frequent updates and new features without hindering the user experience. Tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and others enable changes to be delivered seamlessly.
Automated testing within CI/CD reduces deployment failure rates by 50%.
According to Fortune Business Insights, the global cloud microservices market was valued at USD 1.54 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to USD 8.33 billion by 2032, with a remarkable CAGR of 20.8% during the forecast period.
Lead the Market with Ecommerce Microservices!
Example of Microservice Architecture in an Ecommerce System Explained
Amazon and eBay are typical examples of online marketplaces that are built using microservices for ecommerce. The essential benefit from this approach allows platforms to carry out a smooth operation, scale up efficiently, handle complex processes, and offer a seamless browsing experience for the users.
Here’s what a translated microservice architecture approach looks like:
1. Product service
- Completely manages the product-related details.
- Updates product catalog.
- Ensures that the stock availability data is updated and accurate.
2. Customer service
- Maintains customer management functions from user accounts to managing login credentials.
- Data privacy is ensured by integrating with authentication systems.
- Customer relationship management processes are handled from inquiries to feedback.
3. Payment service
- Manages payment-related functions for all the purchases.
- Processes payments securely by integrating with third-party payments.
- Financial transactions and payment exchanges are validated and ensured of their correct processing.
4. Order service
- Complete purchasing process is monitored from carting to checkout process.
- Coordinates with inventory and payment services for order processing.
- Enables correct delivery of order status and its related information.
5. Inventory service
- Real-time stock availability is checked for accurate display of product information.
- Customers can plan their purchase when accurate stock levels are projected.
- Alerts are triggered for restocking when stock levels run out.
The underlying purpose of delivering a smooth experience to the user is realized with microservice architecture. This level of flexibility has truly advanced the development and utilization of the enterprise ecommerce platform.
On realizing the benefits of its implementation, the adoption rates of ecommerce microservices architecture have increased, with over 92% of the businesses experiencing success in their implementation.
To support the growth, the increasing adoption of serverless architecture, IoT integration, security measures and the focus on sustainability can be attributed. With a predicted CAGR of 19.7 from 2024 – 2033 the trajectory seems to be increasing owing to its growth drivers.
These advancements highlight the potential of ecommerce microservices architecture, emphasizing its role as a reliable approach to commerce platform setup.
Ecommerce Microservices Architecture vs Traditional Architecture
The table below outlines the primary distinctions between e commerce microservices architecture and traditional architecture, focusing on structure, scalability, and system efficiency.
| Aspect | Ecommerce Microservices Architecture | Traditional Architecture |
| Structure | Composed of small, independent services communicating via APIs. | Operates as a single, unified system. |
| Flexibility and Scalability | Highly flexible and scalable; adapts easily to changes. | Limited scalability and less adaptability. |
| Maintenance and Updates | Easier to troubleshoot and maintain due to service isolation. | Issues in one area can impact the entire system. |
| Modular Design | New services can be added or removed without disrupting operations. | Adding or removing components affects the whole system. |
Top 10 Principles & Features of Microservices in Ecommerce
1. Single Responsibility Principle
Each microservice focuses on a specific business capability that ensures that services remain small, manageable, and easier to understand. All of them eventually contribute to a more robust and scalable system.
Companies adhering to the Single Responsibility Principle in microservices report a 30% faster debugging time due to the modularity of services.
2. Autonomy
They operate with complete independence by having their own data storage and managing their own data. As a result, services are developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
75% of businesses implementing autonomous microservices experience 50% fewer cross-team dependencies, leading to faster development cycles.
3. Decentralized Data Management
They work based on complete ownership of a database system that can drastically prevent bottlenecks and has increased resilience.
60% of organizations report an improvement in system performance due to reduced database bottlenecks.
4. API-First Design
Microservices for ecommerce use APIs to communicate with each other, using HTTP/REST for synchronous communication or messaging queues for asynchronous messaging. This approach simplifies integration.
Ecommerce platforms with API-driven microservices gain 30% improvement in system interoperability and flexibility.
5. Scalability
Horizontal scaling can be done based on their specific needs and load by enabling individual services to scale independently.
Horizontal scalability helps Amazon handle over 2 billion requests per day without significant performance drops.
6. Fault Isolation
The overall robustness and reliability of the application are not compromised as these modern ecommerce architecture are independent units themselves, so a failure in one doesn’t necessarily affect others.
Applications built on microservices architectures report 99.95% uptime, even when individual services fail.
7. Continuous Deployment and Integration (CI/CD)
Changes to one service require rapid and reliable deployment of updates without disrupting the entire system, so ecommerce microservices architecture necessitates continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD).
Microservices with CI/CD practices ensure 40% faster time-to-market for new features.
8. Technology Diversity
Different technologies, languages, and supportive frameworks are utilized by different ecommerce microservices. This enhanced flexibility allows for opting for the most feasible tool for each specific service.
This diversity enables 32% lower dependency on vendor-specific technologies, increasing flexibility.
9. Observability and Monitoring
Managing the health and performance of commerce microservices is essential by using effective logging, monitoring, and tracing techniques. Tools and practices are kept in place to ensure visibility across all services.
Logging and monitoring solutions for microservices help achieve 80% faster detection and resolution of performance issues.
10. Design For Failure
Microservices architecture for ecommerce is prone to failures, so strategies for degradation, retries, and circuit breakers need to be implemented to manage and mitigate these failures.
Systems implementing fault-tolerant designs report a 70% reduction in service disruption due to automatic retries and circuit breakers.
Read More: Microservices Architecture: Problems and Solutions with Pattern and Principles
4 Key Benefits of Migrating to Microservices and Headless Commerce for Ecommerce Success

Headless ecommerce refers to separating an ecommerce solution’s front-end and back-end. In another sense, the back-end is entirely separate from the front-end, allowing multiple front-end technologies to communicate with a single back-end through integration.
Microservices are software architecture in which large applications are up of short, self-contained services. This software development method encourages modularity and scalability while allowing for frequent deployments.
1. High front-end traffic does not affect the back-end
One distinct advantage of a microservices architecture is that It can scale the front-end and back-end separately. Developers can add services where they are without having to change the entire system. Heavy traffic on the front end does not affect back-end operations.
2. Increased customization and personalization options
A headless system allows you to connect multiple front-ends to a single back-end system. It opens up possibilities for adding a slew of new front-end touchpoints.
3. Get what you need
A monolith is a feature-rich, all-in-one system, but you may find yourself paying for and working around features and functionality your company does not require. Each microservice in a microservices approach serves a business function.
You can only add what you will use to your system, resulting in a leaner and more efficient technology stack.
4. The technology stack allows for quick implementation
Because microservices ecommerce architecture or headless systems create a distributed way, it is easier for developers from different teams to collaborate to modify the code base and get to market faster.
Read More: Headless Commerce Definition and Meaning Explained 2025
Disadvantages Microservices Architecture
1. Higher Complexity
Microservices have a lot of benefits, but they are also more complex.
2. Increased Network Traffic
Microservices are primarily dependent on the network for communication because they are created to be self-contained units.
3. Dependency on DevOps
An effective DevOps team must be in place for organizations to succeed with microservices.
How Can Microservices Ecommerce Architecture Can Be Used?
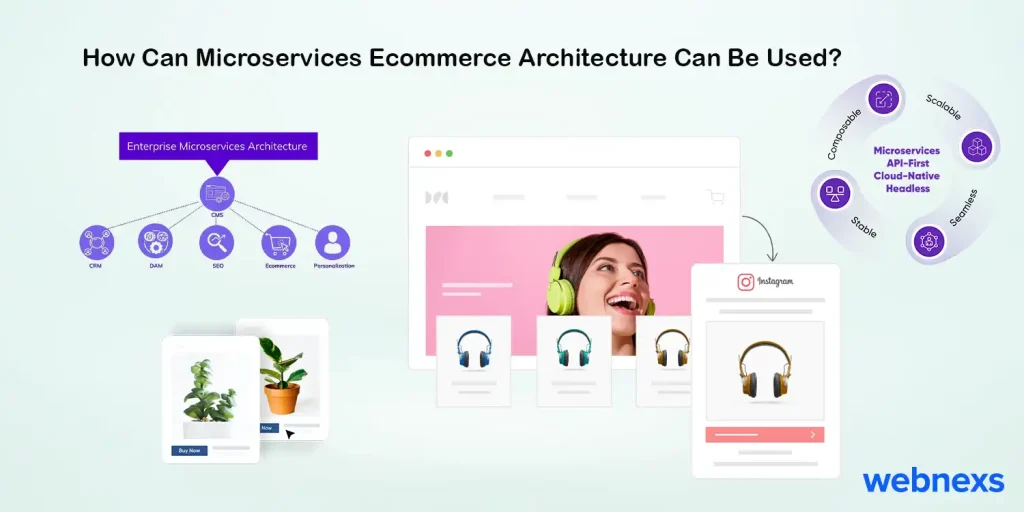
There is no answer to this question because the best way to use an ecommerce microservices structure depends on the business’s specific needs and goals.
1) To divide the large ecommerce platform into smaller, more manageable components.
2) Create a more scalable ecommerce platform to handle traffic and demand spikes more effectively.
3) To create a more adaptable ecommerce platform that can be easily customized and adapted to meet changing market demands, business needs, and customer expectations.
4) Create a more robust ecommerce platform with less downtime and performance issues.
Some little surprises are waiting for you, and that is the disadvantage of the ecommerce microservices architecture. Not as much as you think, but there are some here they are:
An Instance of Successful Deployment of Ecommerce Microservices Architecture
Amazon, a global leader in the ecommerce industry, has realized the advantages of microservices architecture after transitioning from a monolithic setup in the early 2000s. They were able to achieve independent scaling for services like search and payment to ensure reliability during high-traffic events such as Prime Day.
Over 99.9% uptime can be delivered isolating failures and facilitated rapid deployment of new features like Alexa voice shopping. As a result of this shift, optimized resource allocation, reduced costs, and accelerated innovation cycles have been gained which further strengthened Amazon’s position in the market.
You have witnessed the rise and success of a few ecommerce giants across the globe. They have begun their journey with technology that we now consider outdated and have scaled up to deploy cutting-edge ones to optimize the sites.
This limitation is now expelled, as Webnexs currently implements the most advanced technology to elevate your platform to become a successful player alongside Amazon.
Conclusion
Ecommerce Microservice architectures are becoming more popular in the software industry because they enhance scalability and maintainability. These architectures allow you to build a headless ecommerce application that can grow with your business and make migration easier. This article will show you how adopting a microservices approach can benefit your ecommerce platform.
If you have any questions or need help, please reach out us. We’re here to assist you in boosting your sales!





11 Responses
The way you explain a complex topic like modern ecommerce architecture in such an easy-to-understand way is really impressive. Great job!
You are such a natural storyteller. I just love your writing.
That was such thought-provoking content.
The way you explain the complex topic that easily is truly amazing.
I am really impressed with your writing style. Keep it up!??
I can tell this is your best effort!
What a wonderful blog!
This is a very useful blog for me. It offers great insights on microservices for ecommerce. Highly recommended for anyone looking to scale their online store!
Interesting blog!
This is a great analytical blog! It provides valuable insights into how ecommerce microservices architecture can transform online stores for better scalability and efficiency.
Keep up the fantastic work!